Contents
With the increasing trend of businesses going digital, providing international services, and working with virtual teams, the use of cloud technologies is also becoming more common. While this development introduces several fresh attack surfaces, it also provides speed, scalability, and ease. Today’s attackers no longer adhere to historical trends. They employ stolen identities, automation, and multi-step breaches that travel secretly over cloud networks. Companies now depend quite a bit on artificial intelligence in cloud security and the Zero Trust security paradigm to keep ahead as a result of this.
The two approaches supplement each other. Without assuming safety, zero trust checks every user and device. AI reinforces this by observing behavior, spotting discrepancies, and stopping risks before they go viral. Particularly in quickly changing multi-cloud arrangements, they help to create the basis for the future of cloud security.
This thorough manual explains why these two powers count and how businesses can get ready for the upcoming protection era.
WHY CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS NEED A SMARTER APPROACH
Cloud tasks change all the time. Applications interact with dozens of APIs every minute as fresh microservices spin up and elderly ones shut down. With this degree of adaptability, security is more difficult than conventional networks.
- No distinct security boundary
Unlike traditional on-prem solutions, the cloud has no set boundary. Users log in from phones, computers, and uncontrolled devices. This elevates the need of identity-based security above network-based protection.
- Missettings found everywhere in multi-cloud contexts
Still among the most common causes of breaches are insufficient IAM roles, exposed APIs, and incorrectly set storage buckets. Errors increase, and attackers quickly take advantage of them as companies move into Google Cloud, Azure, and AWS.
- Increasing attack founded on identity
Instead of conventional network attacks, most modern ones focus on login credentials, tokens, and wrongly used rights. Managing identities and access becomes the new defense frontline.
These difficulties show why point solutions and conventional firewalls fall short. Cloud security today calls for continual verification, real-time monitoring, and automated threat response, something Zero Trust and AI together provide.
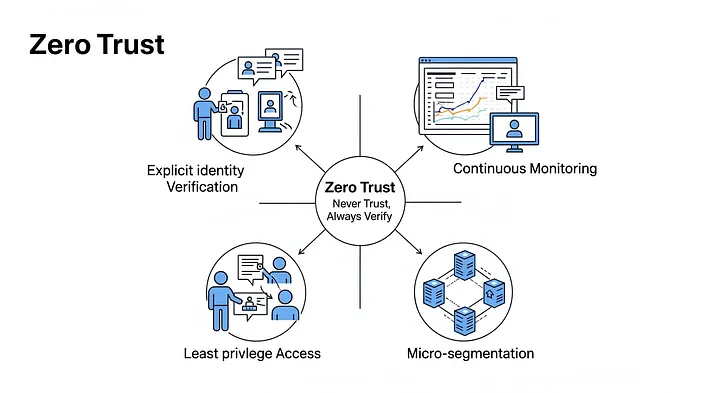
UNDERSTANDING ZERO TRUST IN THE CLOUD
“Never trust, always verify” is the foundation of Zero Trust. It uses continual authentication independent of device or location instead of traditional perimeter-driven security.
- Robust identification verification
Proof of legitimacy is needed for every login request, whether from a service or an employee. This employs risk-based access, MFA, biometrics, and identity governance. Sessions are always monitored for suspicious access patterns even after login.
- Minimum Enforcement of Least Privileged
Zero Trust guarantees that every user, software, or machine only receives the permissions needed to operate. This lowers damage in stolen credentials. Zero Trust blocks the connection absolutely if a developer never requires financial records access.
- Continuous monitoring and logging
Real-time cloud behavior is noted. The system quickly flags any unexpected access of files a user usually avoids. Quick action during suspicious activity is made possible by this continuous visibility.
HOW ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE REINFORCES CLOUD SECURITY
As cloud environments produce more data than human teams can ever analyze, artificial intelligence is becoming absolutely vital. Long before threats become incidents, AI aids in the detection of them, automation of replies, and prevention of incorrect setups.
- Identifying complex dangers
Artificial intelligence analyzes behavior patterns across users, apps, APIs, and networks. It finds aberrations that standard tools miss, including odd data transfers, strange IP origins, or strange login times. This supports detection of early-stage infractions.
- Quicker, automatic incident response
AI can instantly segregate a virtual machine, withdraw tokens, or filter suspicious traffic rather than rely on analyst alert review. These automatic first actions help to stop attacks from spreading and cut downtime.
- Risk prediction and predictive analytics
Based on previous events, artificial intelligence forecasts which assets have the highest risk. It helps security teams proactively correct problems by pointing out inadequate IAM roles, unused privileges, and exposed workloads.
AI AND ZERO TRUST: A POTENT COMBINATION
When both systems collaborate, the company gets a smart and dynamic security architecture.
- More intelligent identity confirmations
While artificial intelligence analyzes behavior patterns, zero trust confirms users. AI sets adaptive authentication or temporary access limitations if someone logs in from a different nation or utilizes a device they have never used before.
- Automated entry judgments
AI constantly assesses user behavior, environmental context, and device health. Zero Trust automatically adjusts rights if something seems dangerous. Access becomes fluid and dynamic, therefore lowering reliance on manual reviews.
- Finding of shadow approach
Hidden hazards, including forgotten administrative accounts, wrongfully assigned service roles, or orphaned policies, are discovered by artificial intelligence scanning of cloud permissions. Often used in sophisticated attacks are these covert access points.
REAL-WORLD APPLICATIONS ACROSS INDUSTRIES
- Financial companies
Banks control sensitive financial data and follow strict compliance requirements. They use artificial intelligence to watch for unusual transactions and Zero Trust to manage staff access.
- Healthcare
Hospitals use IoT devices and safeguard patient information (PHI). AI finds dubious activity on medical equipment, and Zero Trust confirms every patient record access.
- Commerce on the Internet and in shops
Stolen credentials, false accounts, and bot assaults are treated by online vendors. AI lowers fraud attempts; Zero Trust makes certain authorized systems connect to payment servers.
- Hybrid-cloud enterprises
Companies deploying on-prem plus cloud gain from artificial intelligence-driven visibility coupled with Zero Trust’s centralized identification controls.
WHAT THE FUTURE LOOKS LIKE
Automation driven by artificial intelligence, identity-first security, and adaptive Zero Trust controls will dominate cloud security going forward.
What will we see:
- Deployments of cloud systems with self-healing capabilities
- Tools for Red Teaming Guided by Artificial Intelligence
- Completely automated identity governance
- Smart microsegmentation
- Real-time global threat intelligence feeding artificial intelligence systems
Early adoption of this change will give businesses a head start in cybersecurity in the next decade.
AI VS ZERO TRUST VS COMBINED APPROACH
| Feature | AI in Cloud Security | Zero Trust | Combined Strength |
| Identity Protection | Behaviour-based detection | Strict access control | Adaptive identity verification |
| Threat Detection | Detects anomalies and patterns | Limits movement | Stops attacks early and contains them |
| Access Management | Predictive risk scoring | Least privilege | Dynamic, automated access |
| Response Time | Automated actions | Policy-based controls | Fast containment with minimal downtime |
| Multi-cloud Security | Analyses cloud logs | Consistent access rules | Unified oversight across all clouds |
CONCLUSION
Moving toward a future formed by artificial intelligence and zero trust cloud security. While Zero Trust guarantees rigorous access control and ongoing validation, artificial intelligence offers speed, visibility, and behavioral insight. Together, they offer companies better and more flexible protection against growing cloud threats.Expert approval becomes absolutely vital as businesses go further into multi-cloud systems. Organizations can capture misconfigurations, address identity gaps, and safeguard key workloads using their cloud VAPT, zero trust evaluations, and AI-assisted testing.

