Contents
- 1 What Is Antimalware Service Executable?
- 2 Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Consume High RAM and CPU?
- 3 How To Fix Antimalware Service Executable High RAM Usage?
- 3.1 Fix #1 Turn Off Real-Time Protection
- 3.2 Fix #2 Turn Off Scheduled Tasks/Scans
- 3.3 Fix #3 Turn Off Windows Defender AntiSpyware Function
- 3.4 Fix #4 Stop Antimalware Service Executable from Scanning the Windows Defender Folder
- 3.5 Fix #5 Disable Windows Defender and Install A Third-party Antivirus
- 3.6 Fix #6 Update Hardware Drivers
- 4 FAQs
- 5 Conclusion
When our PC slows down, most of us first open Task Manager. Then, we spend a few minutes figuring out which application consumes RAM and CPU resources. More often than not, you can find a single app that is causing the PC slowdown. Other times, you see something else: like Antimalware Service Executable.
It can be a little confusing when you find Antimalware Service Executable with high CPU and RAM usage. The biggest problem is that you do not know where it comes from. What’s worse, you don’t even know if the Antimalware Service Executable process is something malicious. We’ve been there, and we understand the toughness of the situation.
So, to help you out, we have prepared this ultimate guide on how to deal with issues regarding Antimalware Service Executable processes on Windows PCs. More so, we have explained, in detail, how you can fix this issue and bring your device back to normalcy.
Before we jump into the steps, we shall offer some background information about the Antimalware Service Executable process.
What Is Antimalware Service Executable?
Unlike what you may have heard, Antimalware Service Executable is a vital part of the Windows Defender system. As you know, Windows Defender is built into Windows 10 and Windows 11, and it can provide the best protection for your computer from digital threats. Microsoft has included Windows Defender in the OS, so users do not have to purchase a third-party anti-malware or antivirus program.
Therefore, when you see Antimalware Service Executable running on your computer, you can stop worrying about whether it is something problematic. To put it firmly, Antimalware Service Executable is not a virus or malware of any sort. On the other hand, it is one of the elements that keep your computer safe from viruses and other types of malware.
On an ideal day, you do not have to worry about Antimalware Service Executable at all. It should run in the background and take care of the security aspect. However, there are times when the process takes a wrong turn and ends up consuming more CPU and RAM resources than it should.
Why Does Antimalware Service Executable Consume High RAM and CPU?
As an important part of the Windows Defender protection system, Antimalware Service Executable could be responsible for a few features. Some of them are:
Real-Time Protection
The Real-Time Protection module of Windows Defender is designed to protect your computer from digital threats as they become visible in the first place. Whenever your computer gets in contact with a problematic file or website, Real-Time Protection will take action. You do not have to use manual scanning to make this work. It also means the Real-Time Protection module must be running all the time, causing the Antimalware Service Executable process to use up more RAM and CPU resources.
Scheduled Scans
Depending on the Windows Defender settings you have selected, it may run automatic scans of the files on your computer. As you can guess, the Antimalware Service Executable process will be responsible for making them work. So, if the Task Scheduler app has too many task entries from Windows Defender, you will see Antimalware Service Executable running all the time.
If you have a high number of files/folders on your PC, the process will consume a lot of resources as well.
AntiSpyware
The AntiSpyware function of Windows Defender can also trigger the Antimalware Service Executable tasks. The important thing is that the AntiSpyware function may remain active even if you have disabled Windows Defender and different modules. If this function is active, some load will be shared by Antimalware Service Executable, causing a hike in CPU and RAM usage.
In addition to these, other modules of Windows Defender can also keep the Antimalware Service Executable process active. For instance, Windows Defender Cache Maintenance can keep the system running.
How To Fix Antimalware Service Executable High RAM Usage?
Now, based on the ideas explained above, we shall fix the situations when Antimalware Service Executable takes up a high amount of RAM and CPU resources.
Fix #1 Turn Off Real-Time Protection
As you can guess, Real-Time Protection is one of the most resource-consuming tasks of Windows Defender. It is also the most common reason why Antimalware Service Executable takes up a lot of CPU/RAM resources on your PC. Therefore, turning off real-time protection can fix the Antimalware Service Executable high RAM consumption issue for the time being. You can follow the steps given below:
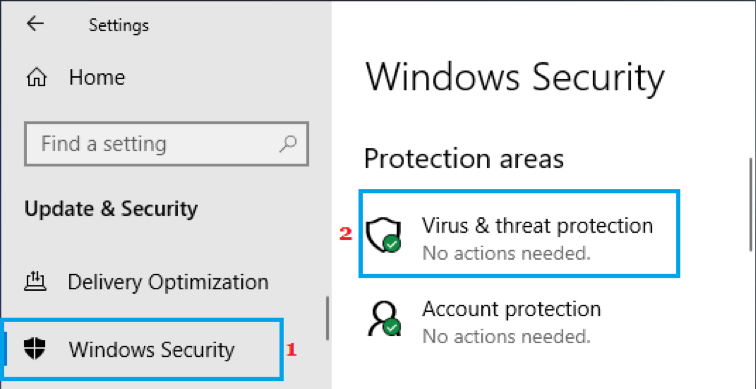
- Open the Start Menu and search for Windows Security.
- On the screen, click Virus & threat protection.

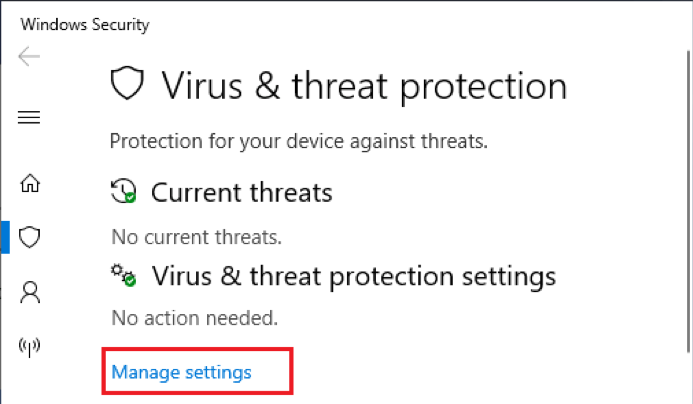
- On the upcoming page, click the Manage Settings button.

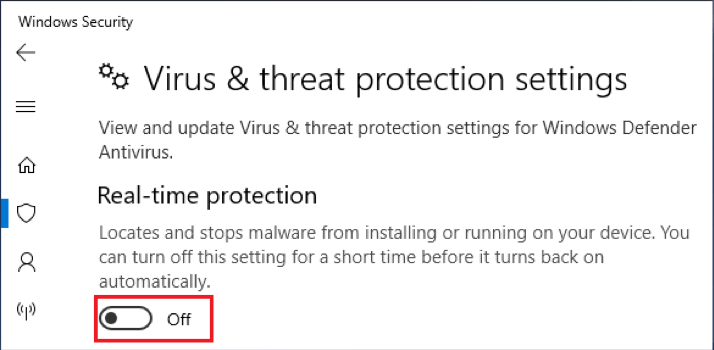
- Now, make sure that you turn off Real-time protection.

You should remember that this process does not disable the Real-time protection module permanently. On the other hand, the Real-time protection module will become inactive for a temporary period—until you restart the computer. When you restart the computer, Windows Defender will automatically activate the Real-time protection module.
Risks: The biggest risk here is that real-time protection cannot protect you any longer. It means you will not receive notifications when you accidentally install or open malware on your computer. Therefore, we do not recommend keeping it turned off permanently.
Fix #2 Turn Off Scheduled Tasks/Scans
Scheduled scans from Windows Defender can also cause the Antimalware Service Executable to consume a lot of system resources. If you are confident about your digital practices and the lack of malware on your PC, you can turn off these scheduled scans using Task Scheduler. It should help you reduce the system usage on your computer.
The steps you have to follow are simple:
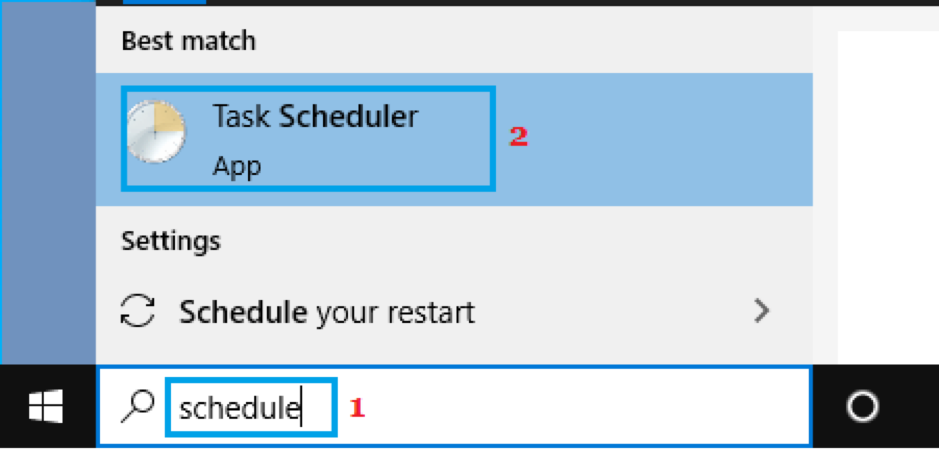
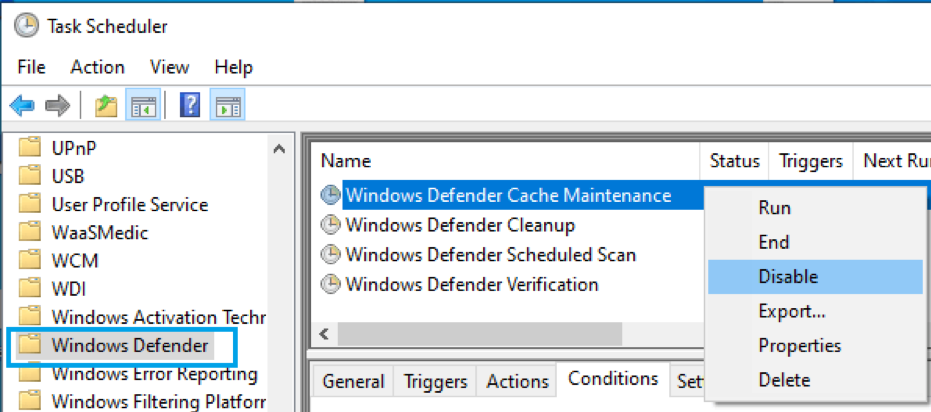
- Open Start Menu and search for Task Scheduler.

- Open Task Scheduler and locate the Windows Defender folder on the left sidebar.

- On the right side, locate Windows Defender tasks
- Right-click on each of these entries and Disable them
From now onwards, Windows Defender will not automatically scan your computer for viruses/malware. As a result, the load on the Antimalware Service Executable will become lower, thus freeing up RAM and CPU resources.
Fix #3 Turn Off Windows Defender AntiSpyware Function
If the above two methods do not solve the Antimalware Service Executable error, you should try turning off the AntiSpyware function of Windows Defender. To do it, however, you need to make changes to Windows Registry. The steps are:
- Open the Start Menu and open Run
- Enter ‘regedit’ and run the command
- Once you open the Registry Editor, navigate to the following path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender
- Double-click on the entry named DisableAntiSpyware.

- Change its value from 0 to 1.
It means you have successfully turned off the AntiSpyware function of Windows Defender. Please remember that it will make your system more prone to spyware threats.
Fix #4 Stop Antimalware Service Executable from Scanning the Windows Defender Folder
Sometimes, the Antimalware Service Executable process will scan the Windows Defender folder, which has a lot of data. As a result, the process will need more RAM and CPU resources. Therefore, a logical way to fix the Antimalware Service Executable with high CPU and RAM usage error is to exclude the Windows Defender folder from the scanning list of Windows Defender. To do it,
- Open Windows Security from the Start Menu.
- Open Virus & threat protection.

- Choose Manage Settings from the page.
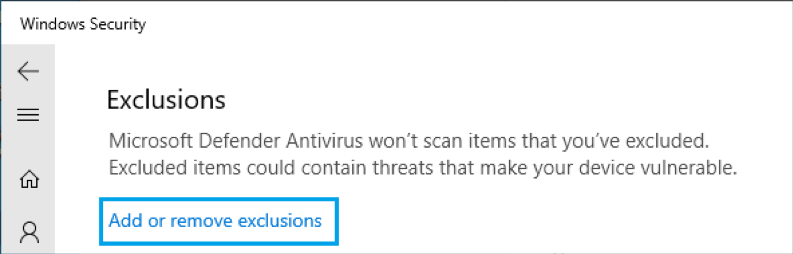
- Go to the Exclusions subsection.

- Click Add or remove exclusions and choose Folder.
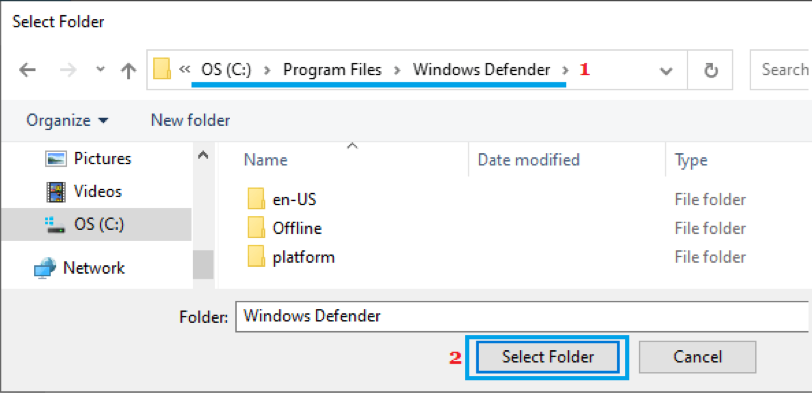
- Now, navigate to C: Program Files/Windows Defender.

- Select the folder, and restart your computer.
Now onwards, Antimalware Service Executable will not scan the Windows Defender folder, meaning you do not have to worry about high CPU or RAM usage.
Fix #5 Disable Windows Defender and Install A Third-party Antivirus
As you may have noticed, the biggest cause for Antimalware Service Executable is the non-optimized nature of Windows Defender and its components. Of course, you can follow the methods we have mentioned above to change how Windows Defender works. But, in addition to being tedious, these steps will affect the overall security of your computer.
Therefore, it makes more sense to disable Windows Defender and forget about the Antimalware Service Executable errors, once and for all. And, if you are wondering how you can disable Windows Defender, it is easy.
You can download and install a third-party antimalware program on your computer, and Windows Defender will automatically turn off. Because two antivirus programs cannot run on your computer at the same time, Windows Defender will disable all related functions as well.
By the way, you should make sure that you download and install an efficient antivirus program. If the third-party antivirus program consumes more resources than Windows Defender, you will be back to square one. Therefore, when you explore free and paid antivirus programs available for Windows, choose one that suits your requirements.
Fix #6 Update Hardware Drivers
If you continue the face the Antimalware Service Executable high usage issue even after installing third-party antivirus programs, you should take some additional steps to fix the issue. Here are a couple of them:
- You should update the hardware drivers to make sure that hardware issues are not causing Windows Defender to malfunction
- It may be a good idea to consider reinstalling or resetting your Windows PC. Accidental changes to the system can be revised, and you can have a near-fresh PC experience.
- Last but not least, you should update Microsoft Windows to the latest version along with all available supplementary upgrades. It will make sure that you get a bug-free Windows experience.
With these ultimate steps, you should be able to fix the Antimalware Service Executable errors.
FAQs
Q1 – Is it OK to disable antimalware service executable?
Yes, it is okay to disable antimalware service executable for a temporary period. It may help you to reduce the RAM/CPU load of your computer. However, you cannot and should not keep the module deactivated on a long-term basis. If you want to do that, you will have to replace Windows Defender with another antivirus.
Q2 – How do I stop antimalware service executable from using so much CPU?
You can follow a number of methods to stop Antimalware Service Executable from using so much CPU. One of the methods is to disable the Antimalware Service Executable process for a temporary period. If the issue persists, you can also consider disabling Windows Defender and installing a third-party antivirus program.
Q3 – Is antimalware service executable a virus?
No, Antimalware Service Executable is not a virus. On the other hand, the Antimalware Service Executable process is an essential part of the Windows Defender system on all Windows PCs. Due t the same reason, it is not wise to disable the Antimalware Service Executable process unless you have installed a supplementary antivirus program.
Q4 – How much RAM does antimalware service executable use?
On average, Antimalware Service Executable should be using a couple of hundred MBs of RAM, but it is tough to provide a fixed figure. For one, the Antimalware Service Executable process is designed to adapt to the changing security requirements of your PC. So, if Windows Defender is running more functions, the process is bound to use more RAM.
Conclusion
We believe we helped you solve the Antimalware Service Executable high RAM and CPU usage errors without much hassle. We have recommended all types of solutions so that you can choose one based on your needs and convenience.
For instance, if you are looking for the easiest method to get rid of the problem, you can go ahead and disable Windows Defender.
On the other hand, if you do not mind making some extra effort, it is possible to disable separate elements of Windows Defender and make Antimalware Service Executable take up fewer system resources.