Contents
Windows supports a wide range of file extensions, which are essentially the different types of files that it can read and write. These extensions include TXT, DOC, XLS, JPG, and many others. Each extension corresponds to a particular type of file that Windows recognizes. In order to open or save a file with a specific extension, you need to have the right program installed on your computer.
There are literally thousands of different file extensions used by Windows and other operating systems, so it’s impossible to list them all here. However, some of the more common ones that you’re likely to encounter include:
TXT

A text file that contains nothing but plain text. For example, a TXT file might be created in Notepad or Wordpad.
DOC

A document file created in Microsoft Word. DOC files can contain text, images, and other formatting information.
XLS

An Excel spreadsheet file created in Microsoft Excel. XLS files can contain data, formulas, and other information.

A Portable Document Format file. PDF files can be viewed with a PDF reader such as Adobe Reader.
PPT or PPTX

A PowerPoint presentation file created in Microsoft PowerPoint. PPT files can contain text, images, formulas, charts, graphs, and other information.
JPG

A JPEG image file. JPG files are typically created by digital cameras or scanners.
GIF

A GIF image file. GIF files are often used for small, web-friendly images.
PNG

A PNG image file. PNG files are often used for larger, high-quality images.
MP3

An MP3 audio file. MP3 files can be played by media players such as Windows Media Player or iTunes.
WAV

A WAV audio file. WAV files are typically much larger than MP3 files and are not as widely used.
MOV
A QuickTime movie file. MOV files can be played by media players such as Windows Media Player or iTunes.
AVI

An AVI video file. AVI files can be played by media players such as Windows Media Player or VLC Media Player.
ZIP

A ZIP file. ZIP files can be opened with programs such as WinZip or 7-Zip.
RAR
A RAR file. RAR files can be opened with programs such as WinRAR or 7-Zip.
EXE

An executable file. EXE files are programs that can be run on your computer. For example, auto clicker exe.
DLL

A dynamic link library file. DLL files are libraries of code that can be used by other programs.
SYS

A Windows system file. SYS files are essential to the proper functioning of Windows.
You’re likely to encounter many other file extensions while using Windows. However, the above list includes some of the most common ones that you’ll come across.
How to Open a File on Windows
To open a file on Windows, you need to have the right program installed on your computer. For example, if you try to open a DOC file in Notepad, you’ll see an error message saying that Windows can’t open the file. In order to open the file, you need to have Microsoft Word installed on your computer. Similarly, if you try to open an XLS file in Microsoft Word, you’ll see an error message saying that the program can’t open the file. In order to open the file, you need to have Microsoft Excel installed on your computer.
If you’re not sure what program should be used to open a particular file, you can try using one of the free file viewers available online. Otherwise, you can simply search for the file extension on Google to find out more.
How to Save a File on Windows
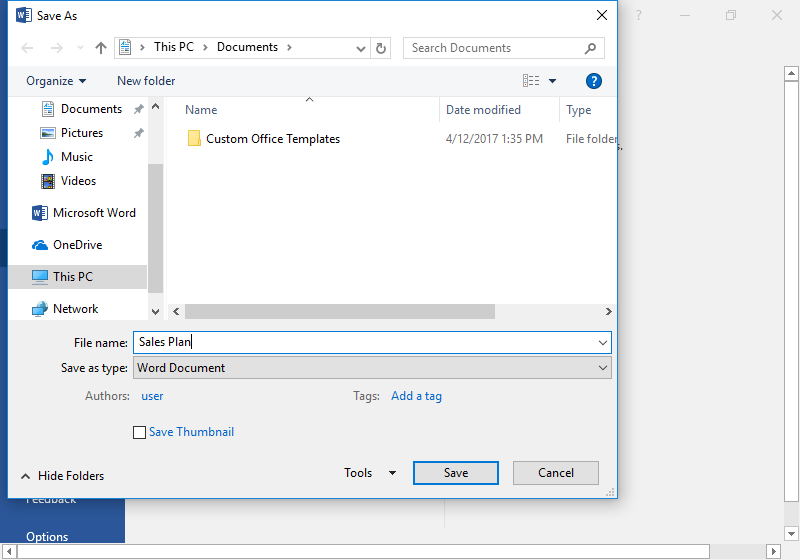
When you save a file on Windows, you need to specify the file extension that you want to use. For example, if you’re saving a document as a DOC file, you need to specify the .doc file extension. If you’re saving an Excel spreadsheet as an XLS file, you need to specify the .xls file extension.
When you save a file, you’ll also need to specify where you want to save it. For example, you might save a file on your computer’s hard drive, on a USB flash drive, or on a network drive. You can also save files in different formats, such as PDF or XML.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s important to know about the different file extensions used by Windows and other operating systems. File extensions are used to specify the type of file that you’re working with. They can also be used to determine which program should be used to open or save a particular file. Finally, when you save a file on Windows, you’ll need to specify the file extension that you want to use.

